A cenotaph to lost Royal Navy personnel – a National Historic Site of Canada – and archival records that show that it is made from an American shipwreck! Readers may recall the very origins of this website were to help explore and add provenance to relics and artifacts connected to Canadian military cenotaphs. So in a sense, after interpreting the history and shipwrecks connected to the lost 1845 Sir John Franklin Expedition in search of a Northwest Passage, we’ve come home!
We recently posted about the history of the “Franklin Cenotaph” at Beechey Island, Nunavut. This isolated monument is an incredibly rare memorial to the crews of the lost 1845 Sir John Franklin Expedition and the searchers who died looking for them. It is identified by Parks Canada as a “character-defining element” of the Beechey Island Sites National Historic Site of Canada. It is important to understand what the cenotaph is and what components combine to create it.
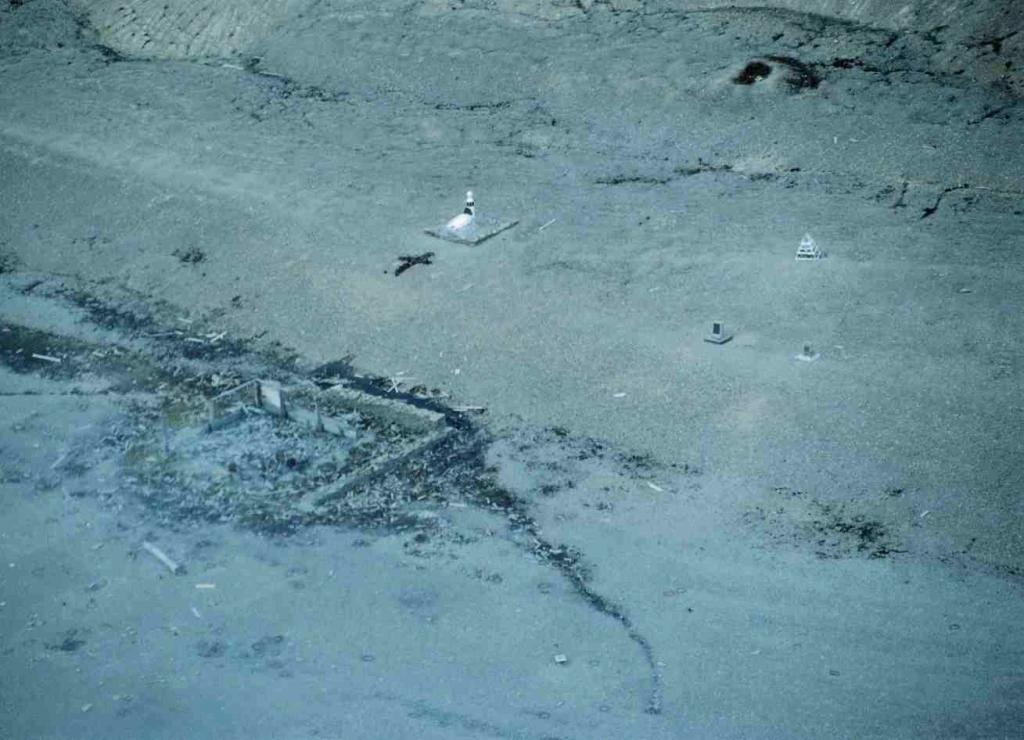

The column itself, built in the arctic summer of 1854, under the direction of Captain W.J.S. Pullen, HMS North Star, is thought to be made out of the machinery of a lost American whaling ship, the McLellan. This little-known detail further solidifies the Anglo-American character of the commemorative program of the monument.* We ended our earlier post with a series of questions we hoped could be answered about the column’s origins. We also wondered if it really could have been made out of the capstan of the McLellan, as has been reported.** A capstan, as defined by wikipedia is “a vertical-axled rotating machine developed for use on sailing ships to multiply the pulling force of seamen when hauling ropes, cables, and hawsers.”

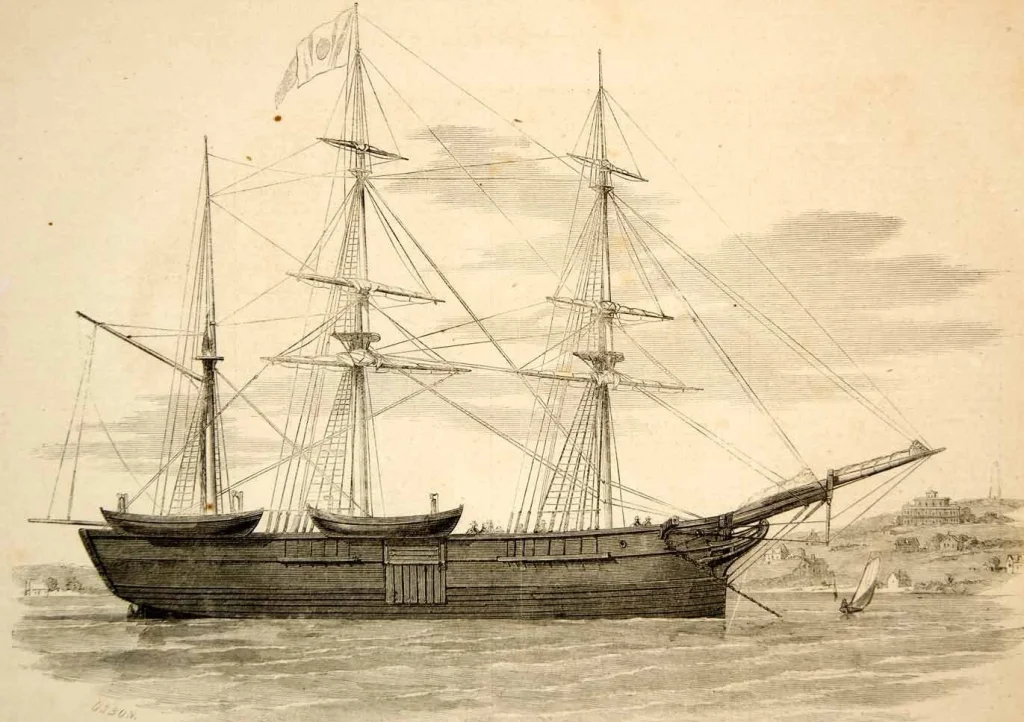
McLellan was a 366-ton barque-rigged wooden ship which had served as a general merchant in the 1830s, but had been purchased by the firm Perkins & Smith for the bowhead whaling industry in 1846. It was homeported out of New London, Connecticut, under the command of Captain William Quayle.*** We recently had an opportunity to closely examine a work at Library and Archives Canada which depicts the July 1852 loss of this ship:
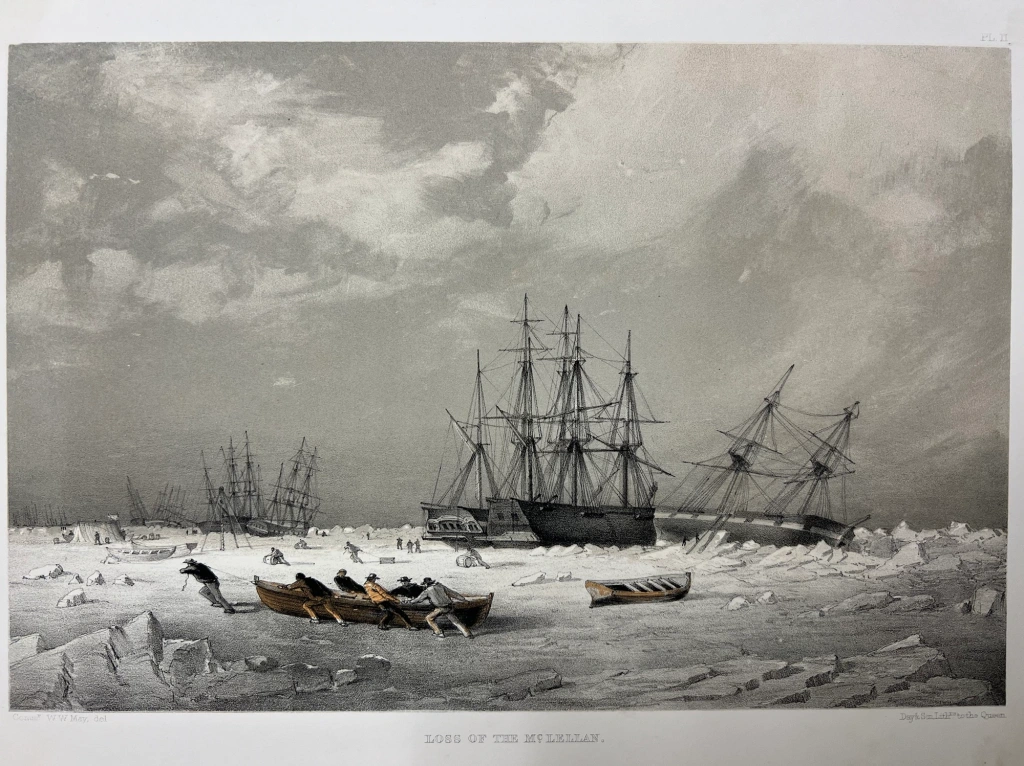

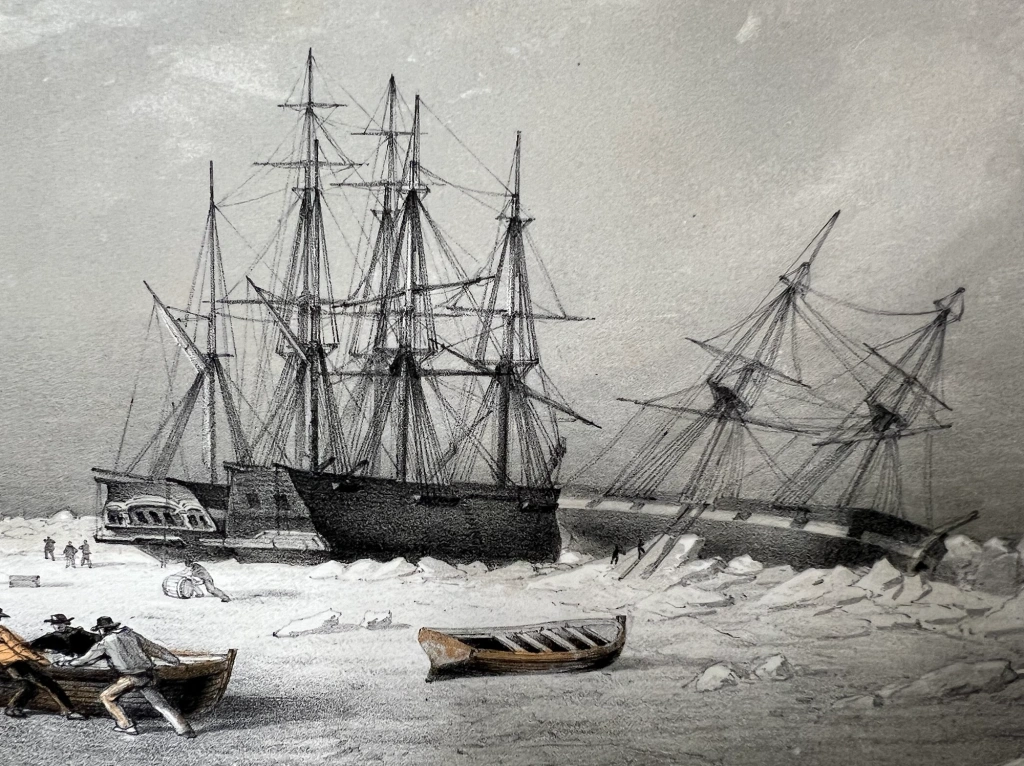
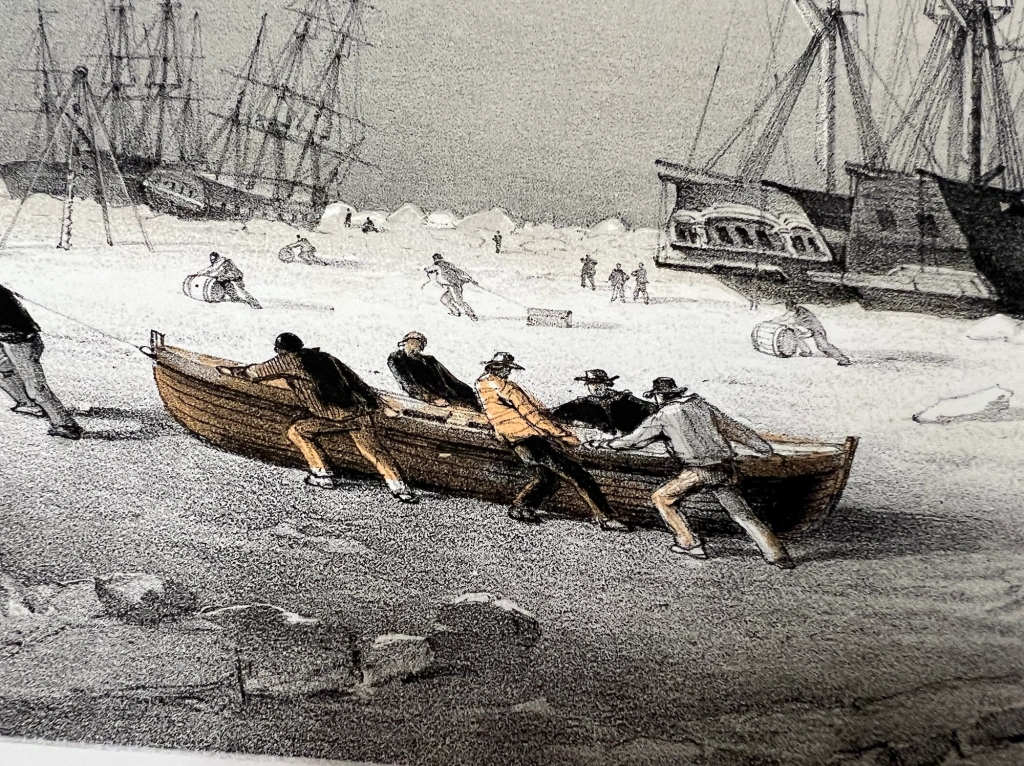
The engraving, made from a sketch by Cmdr. Walter W. May – who witnessed the events –includes many interesting details of whaling ships beset in ice near each other, and Royal Navy vessels. It also shows crew members salvaging items from a visibly-damaged ship.

During the 1851 season, McLellan had been involved in a milestone in the development of the American whaling industry. Quayle had landed a shore party, led by mate Sydney O. Budington, at Nimegen Island, Cumberland Sound. This small group built a stout structure there and hunkered down to overwinter. With the assistance of local Inuit families, crew were able to live in relative comfort into 1852, trading for items and swapping their clothes for warmer furs.****
The plan was for the group to begin whaling far earlier than any ship-based crew could gain access to the area. It was a bold plan and it worked – they were able to land a huge catch of seventeen bowheads. They also became the first commercial interest to overwinter in the Canadian Arctic since the 16th Century voyages of Martin Frobisher. This shore party stayed on until September of 1852, and would eventually have to be taken off by another whaling ship.

At the beginning of the 1852 season, McLellan, on the return voyage to the whaling grounds and to pick up Budington’s party, was one of a group of whaling ships that were beset in ice in the Davis Strait near Melville Bay. The ships were in a perilous position, between the land ice and the shifting sea floes. Sir Edward Belcher’s Arctic Squadron, comprising HM Ships North Star, Assistance, Resolute, Pioneer, and Intrepid, were on their way up to Lancaster Sound to launch a sustained effort to locate Sir John Franklin and the crews of HMS Erebus and Terror (by this time missing for seven years). On June 20th, just as the naval squadron was coming up with the group of whalers, the veteran Kirkaldy whaling ship Regalia was crushed by ice. What followed seems unusual nowadays, but was apparently the accepted practice: The ship was quickly stripped of valuables, crew set out to find another whaler to serve in, something of a party broke out on the ice, and the hulk was burned to ensure it would not menace other ships.
In early July, McLellan ran afoul of North Star, the depot ship of the Expedition, and the Alexander, a Dundee whaler. It damaged the cathead of the North Star, and the bowprit of the Alexander. The mizzen mast of McLellan had to be cut away to avoid further damage. The American whaler was severely nipped by the encroaching ice. The crew were preparing to abandon ship and the whalers in the area looked forward to commencing the usual “sacking and burning.” Instead, Belcher purchased the damaged vessel from Captain Quayle. The Royal Navy crews set about repairing the whaler. The repairs held until the ship was nipped more forcibly on 8 July. McLellan was gradually crushed over the next week. Naval crews salvaged spars, stout timbers, fittings, machinery, and cargo from their newly-purchased hulk. Valuable items were shifted over to North Star and the search ships.

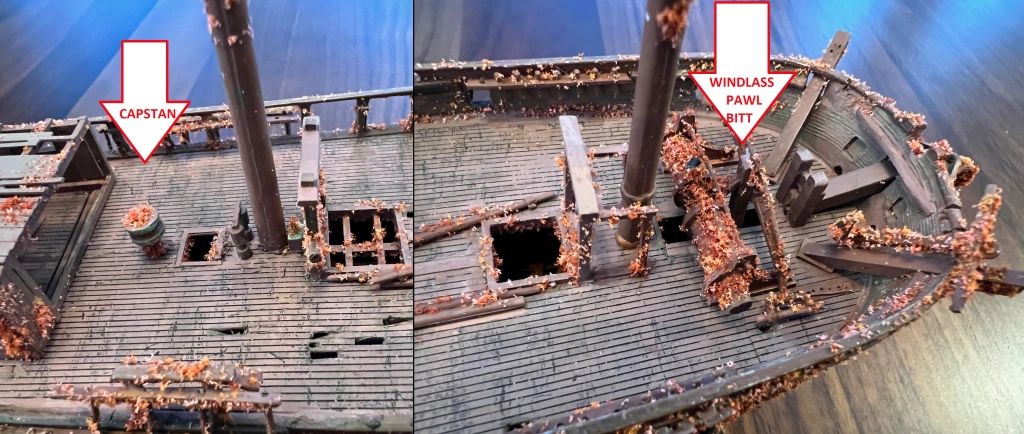
Two years later, these parts were a ready source of materials for the program of construction and “beautification” that Belcher and W.J.S. Pullen organized at Beechey Island, the site of the Expedition’s depot. We originally believed that the (interior) spindle of McLellan’s capstan had been transformed into the central element to the Franklin Cenotaph. At the time of our earlier post, we were concerned about one issue: not all whaling ships had capstans. For example, the most similar ship to McLellan remaining in existence, the Charles W. Morgan, isn’t fitted out with this prominent piece of machinery. To effectively operate a capstan, a ship required a large crew. Many merchant ships favoured the use of their windlasses, which could be operated with their smaller crews. A windlass, normally situated near the bows, forward or immediately aft of the foremast, is “ A mechanism operating on the same principle as the capstan, but on a horizontal axis, used on board merchant ships, and some smaller vessels of the royal Navy, for weighing the anchor, hoisting and hauling.”*****
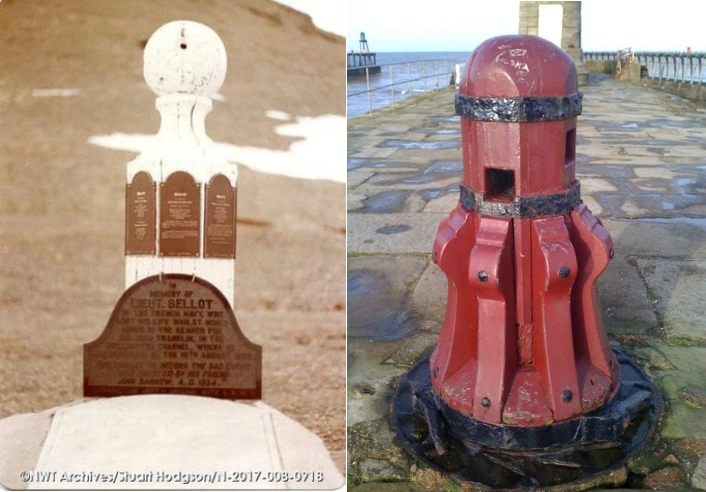
Resolute’s apprentice carpenter, William T. Mumford, the subject of our recent post, was an active participant both in the July 1852 salvage of McLellan, and in building the cenotaph during June 1854. He had just arrived back to Beechey after the mid-May abandonment of Resolute off Dealey Island. Mumford’s information, from his records at Library and Archives Canada, has helped us update the provenance of this important memorial. He wrote in his diary on Saturday, June 24th, 1854: “Midsummer Day, Light breeze from the E-N-E full in the forenoon but hazy with sleet in the afternoon. No water on the floe, and the pools on the land coated with ice. Hands cleaned main & lower decks carpenters employed trimming the Pawl Bitt of the McLellan for a monument to the memory of those who died and are buried elsewhere.“
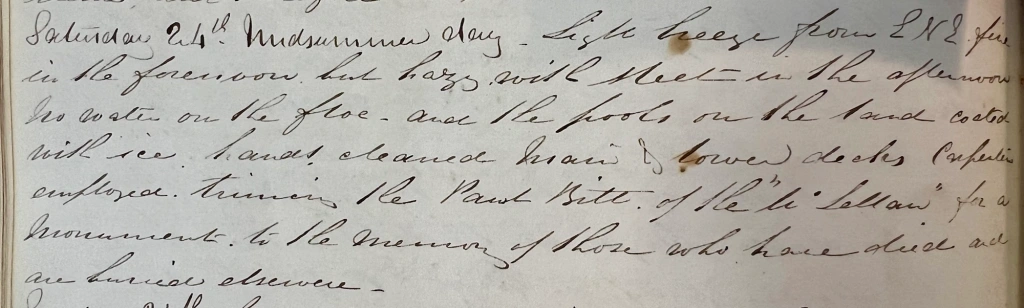
More than almost any other member of the Belcher expedition, Mumford’s occupation and prior experiences make him the expert on the origins of the central monument at Beechey. The “Pawl Bitt” was a strong timber, normally square, that was an important part of a ship’s windlass in the era of wooden sailing ships. It supported the “pawl”, a strong ratchet that ensured that leverage gained by the rotation of the windlass barrel was not lost. The pawl bitt was a substantial structural timber that usually connected straight down to the lower deck. It also usually supported the ornamental bracket the ship’s bell was hung off. This made it an important ceremonial and commemorative site. In this case, the Belcher Expedition carpenters’ efforts at “trimming” seems to have involved carefully working the square timber into an octagonal column, creating a finial ball to surmount the column, carving out or adapting some cavity to house the idiosyncratic “postal office” plaque now located at the rear of the column, and installing the original eight dedicatory plaques to memorialize lost crew members (which are individually identified in a note in our earlier post).

As we hope we have shown with both posts about the “Franklin Cenotaph,” this memorial is a powerful site of memory of a great era of polar exploration history. As a very early example of a military cenotaph, it has much in common with First World War battlefield memorials. It was constructed from relics and materials on hand, by comrades who knew the lost and the missing. Ship’s Carpenter William Mumford’s diary has helped enrich the provenance of this important monument by linking it to an identified feature of the wrecked American whaling ship McLellan. We hope that visitors to Beechey Island, Nunavut, who stand in contemplation before the cenotaph can better appreciate this remarkable artifact. To paraphrase a oft-repeated inscription from other memorials: HERE SEARCHED BRAVE SAILORS – YOU WHO TREAD THEIR FOOTSTEPS REMEMBER THEIR GLORY.
*An inscription added later recognizes Anglo-American cooperation in the search efforts over the High Arctic. The United States participated in search efforts such as the two Grinnell expeditions, and Elisha Kent Kane’s later searches. The 1858 addition to the monument of Lady Franklin’s marble (eventually brought up by Captain Leopold McClintock) expresses the shared Anglo-American concern for establishing the fate of the Franklin crews.
**The link between the Belcher column and McLellan is noted in Barr and Stein’s January 2017 article “Frederick J. Krabbé, last man to see HMS Investigator afloat, May 1854” Journal of the Hakluyt Society. (P27) The authors appear to have consulted Mumford’s diary, but mention the source of the column is McLellan’s capstan drum.
***This description of McLellan’s wrecking draws extensively from information in Philip Goldring’s Jan-Feb. 1986 Beaver Magazine article “The Last Voyage of the McLellan” PP39-44. The issue is currently accessible at the Canada’s History Magazine archive: https://www.canadashistoryarchive.ca/canadas-history/canadas-history-feb-mar-2019/flipbook/1/ Captain (later Colonel) William Quayle had a remarkable life, before and after his four years with McLellan, with many notable events outlined in a 20 June 1901 Moberly Weekly Monitor profile of him: https://www.newspapers.com/article/moberly-weekly-monitor-william-quayle/66609/ that article also gives Quayle’s description of McLellan as having been a barque of 110 feet overall length, 27 feet 7 inches wide, 14 feet nine inches deep, of about 326 tons.
****McLellan and the other American whalers had more diverse crews than mid-Victorian Royal Navy ships. It would be interesting to know if Budington’s shore party had brought Black whalers directly into contact with Inuit families.
***** “Windlass” A Sea of Words ; A Lexicon and companion for Patrick O’Brian’s Seafaring Tales (New York: Owl Books 1997) P.458.



























































































