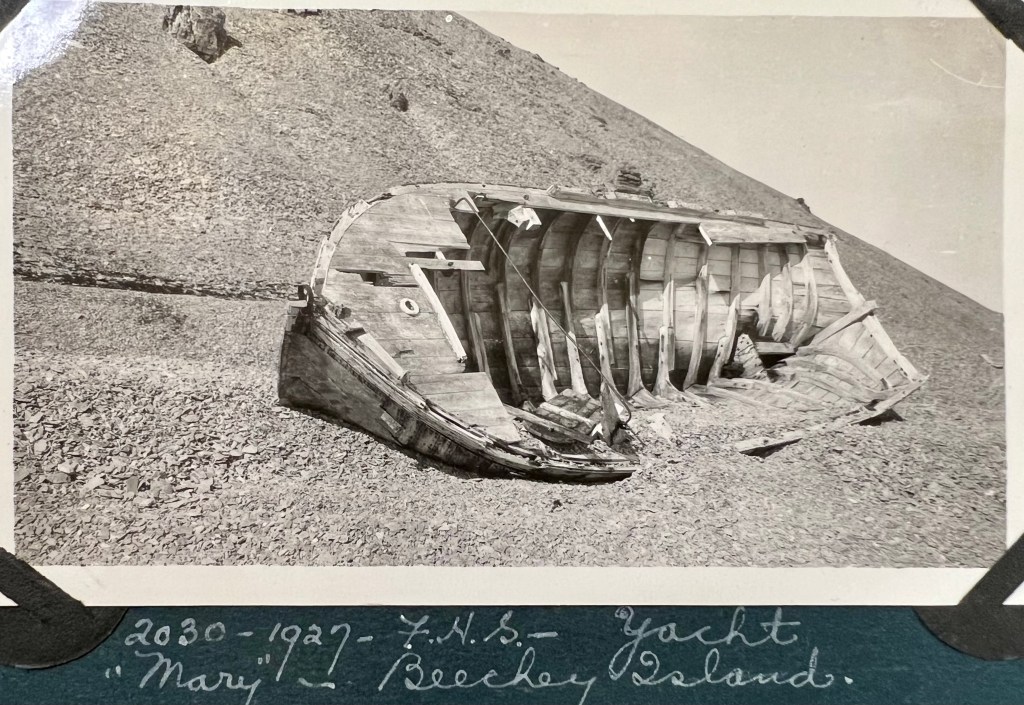

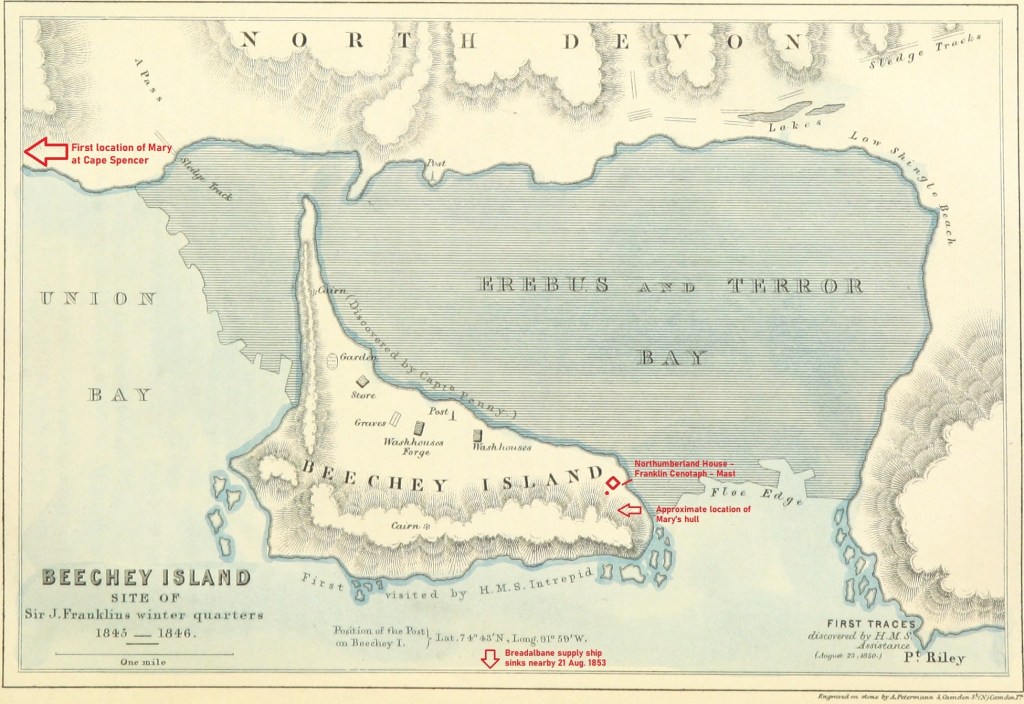
One of the remarkable relics at Beechey Island, connected with the searches for the Sir John Franklin 1845 expedition, is a large mast which has collapsed along the beach, pointing out to Erebus and Terror Bay. This stood for years in front of the ruins of Northumberland House and a motley collection of memorials. Beechey Island is an isolated, barren place, just off the southwest coast of Devon Island, in the High Arctic, in present-day Nunavut. It had been the site of the Franklin Expedition’s first winter encampment, when HM ships Erebus and Terror had sought shelter here in 1845 and been frozen-in. In 1846, before the Bay released the ships, three members of the Expedition were buried just up the beach. The island and surroundings later became prominent as a staging base/supply depot in the expeditions sent to try and ascertain the fate of Franklin and his crews. More searchers would die at and around Beechey, and the Breadalbane supply ship would be wrecked nearby in 1853. Today, burials, monuments, ruins and shipwrecks remain.

The mast is a significant artifact with an important story.1 It is reputed to be the last large remnant of the Mary, Sir John Ross’s yacht. This trim little 12-ton cutter-rigged craft had been brought North by Ross, and accompanied his much larger yacht, the brig Felix. It had been built for the trip out, and both it and 70-foot, 100-ton Felix (sometimes referred to as a brig, sometimes a schooner) were reinforced for polar service with strong hulls and iron or zinc hull sheathing. Felix was Ross’s search ship, but Mary was intended for a different purpose.
In August 1850, Sir Horatio Austin’s crews of HMS Resolute and Assistance (accompanied by HM Steamships Pioneer and Intrepid) and Captain William Penny’s ships Lady Franklin and Sophia made exciting discoveries at and around Beechey Island.2 These first traces of the lost expedition invigorated search efforts.
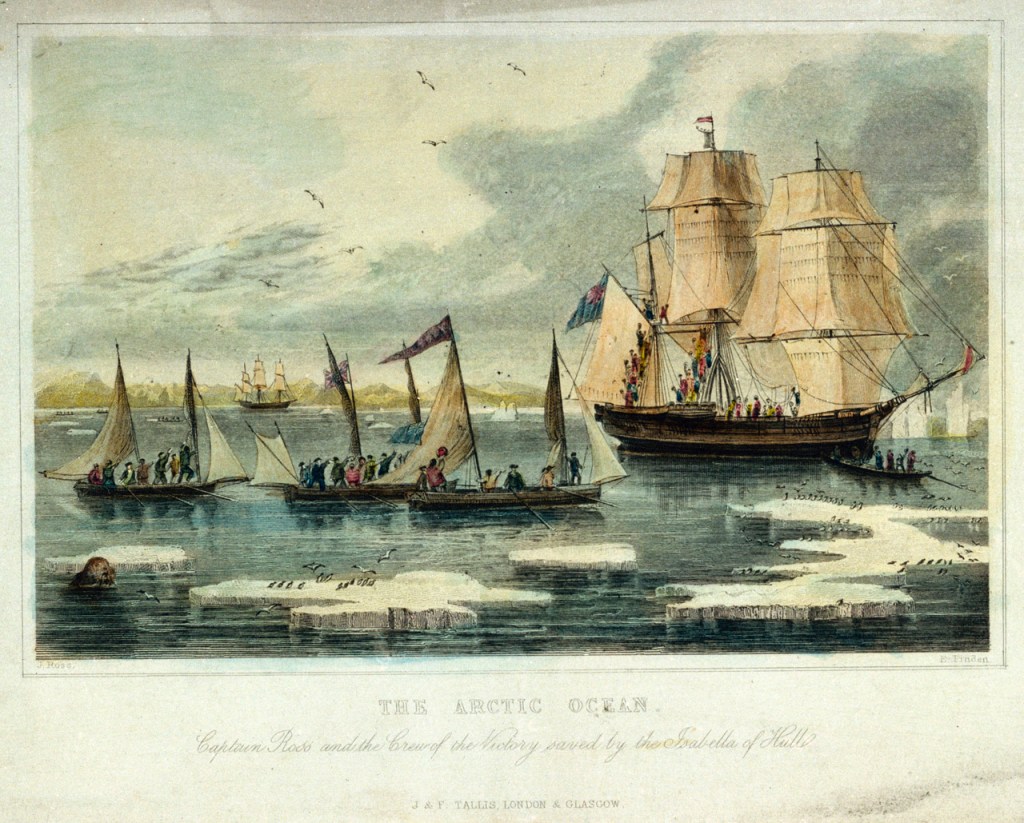
Ross arrived days later in Felix, honouring a promise he had made to come to the aid of Franklin. He was 72 years old, and his sense of duty and concern for his friend brought him out of retirement. When the Admiralty declined his offer to lead an expedition, the Hudson’s Bay Company funded the expedition. His plan, should the lost expedition not be located or turn up, was to leave Mary behind.
Ross knew better than anyone the value of a cache of food and stores and a serviceable boat. On his 1829 expedition, accompanied by his nephew James Clark Ross, his ship Victory had been trapped in ice. Three years later they were forced to abandon their refuge. They retreated to Fury Beach, where they had to spend yet another long, dark winter frozen-in. But Fury Beach was their salvation: Parry’s 1825 expedition had left a cache of supplies and three boats from their wrecked ship, HMS Fury. The boats and supplies allowed an expedition, which had been widely assumed to have ended in death and disaster, to escape to Prince Regent Inlet and rescue. Ross hoped that some similar depot and boat could help Franklin Expedition survivors, or anyone else trapped in the area.

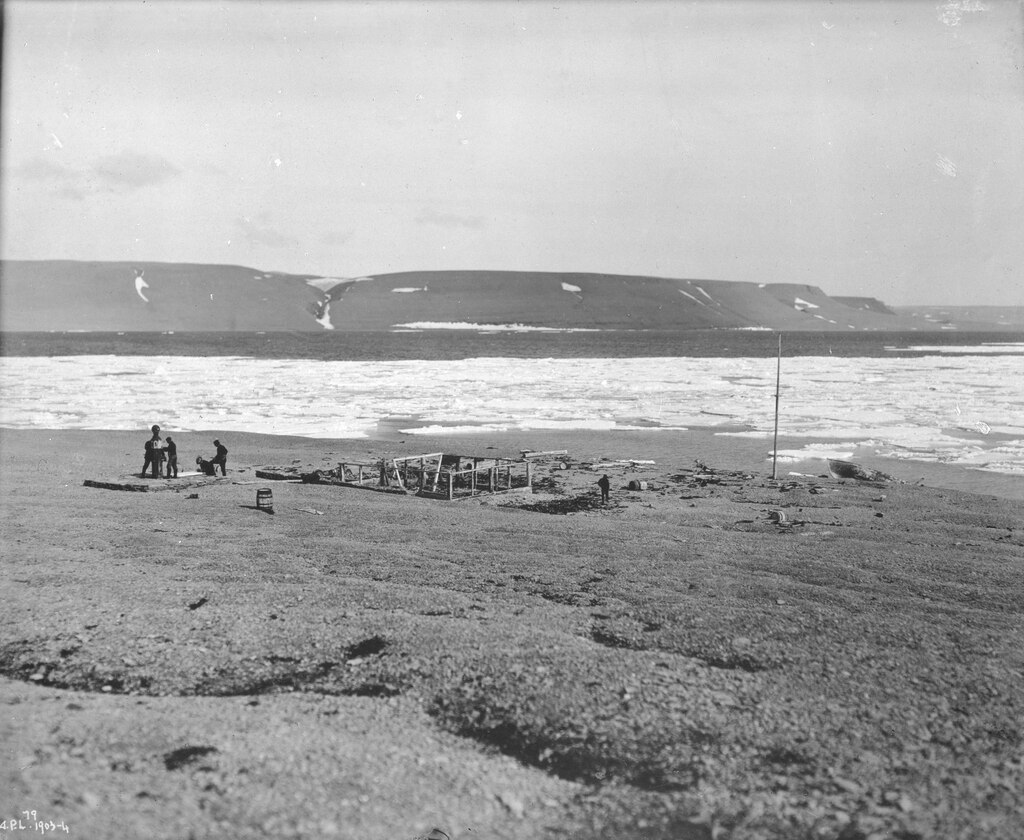
With larger Admiralty-supported expeditions scouring the Arctic, it was time for Ross to return home. Mary was initially left west of Beechey at Cape Spencer, packed with a good store of provisions. The boat was moved soon after to Erebus Harbour when the Edward Belcher expedition incorporated it into new construction. The crew of HMS North Star, the depot ship supplying the Belcher search ships, dragged Mary up the beach and deposited her under Beechey’s soaring cliffs. The yacht was intended as a companion to Northumberland House, which was packed with useful supplies and provisions. Stranded crews that came to Beechey, once they had sheltered and replenished their stocks, could strike off in the yacht in the very short navigation season that those high latitudes allow. Mary and Northumberland House functioned together as their own extraordinarily remote lifesaving establishment. Robert McClure informed the crew of his long-trapped ship, HMS Investigator, that one group would travel to Cape Spencer to board Mary.3 As every one of the Belcher search ships would later need to be abandoned, with their crews completing harrowing marches to safety, the idea had merit.
In 1876, Allen Young, on his second Arctic expedition in the retired gunboat Pandora, found Mary to be in very good shape, still tight and dry and with mast up and sails stowed onboard, in a mostly dry cabin.4 Northumberland House, by comparison, had been damaged and ransacked (reportedly by bears). Young had been one of the last to see this same spot from the Fox, as the navigator on the Capt. Francis Leopold McClintock’s 1858 expedition. With the Pandora’s departure, Mary was again left to her lonely fate.

Occasional visits by notable Arctic explorers continued into the 20th Century. Mary sustained more damage and deterioration and at some point the mast was taken from near the hull and erected in front of Northumberland House, near a large whale boat.5 The hull assumed a prominent list, and the decking deteriorated. Visitors also speeded deterioration by taking a few choice souvenirs. The derelict vessel was photographed in 1923 and 1927, during annual trips to the Arctic by Canadian government ships.

During the 1970s and 80s, the mast leaned at an increasingly rakish angle, until it fell to the ground sometime before 1992. Like everything else at Beechey, the mast is undergoing a very gradual deterioration. We conclude our brief account of a yacht that was intended to serve as a rescue vessel with an important takeaway: If you plan to be shipwrecked in the high latitudes of the Canadian Arctic somewhere around Beechey Island, you can no longer depend on Mary to yacht away from it!
- Season Osborne’s detailed history of Mary “What Happened to the Mary? A Historic Site ravaged through time” (Above and Beyond – Canada’s Arctic Journal 2015/2 pp. 23-27) helped sort out many contradictions. It is available at https://issuu.com/arctic_journal/docs/above_n_beyond_marchapril_2015/ ↩︎
- This is a simplified account of discoveries, for a more fulsome treatment of the moment of the first discoveries at Cape Riley (by Capt. Ommanney of HMS Assistance) and Capt. Penny’s team, including R.A. Goodsir, finding the graves at Beechey, please see Alison Freebairn’s finger-post blog and Logan Zachary’s Illuminator blog on the topic. ↩︎
- George F. McDougall “The Eventful Voyage of H.M. discovery ship “Resolute”…(London: Longman et. al. 1857) P216. McClure ended up encountering the HMS Resolute party sent to look for him under Lt. Pim and evacuating everyone to Resolute). Available at Babel.hathitrust. ↩︎
- The above source refers to the mast as having been moved sometime around the Second World War, but the 1903 photo seems to show a similar mast in front of Northumberland House, which is more substantial than the flag pole that had been on the site during the 1870s. ↩︎
- This section is drawn from Lt. Allen Young’s Cruise of the Pandora; from the private journal kept by Allen Young commander of the expedition (1876; republished by Cambridge University Press 2012). The illustrations are from a copy of the original at Library and Archives Canada. ↩︎