Thirty-five years ago today, during Operation Desert Storm, the Canadian Navy came to the assistance of our US allies, in a characteristically classy way.1 Today, we mark the anniversary of HMCS Athabaskan entering into a mined area of the Persian Gulf to assist the damaged cruiser USS Princeton. This episode marked a meaningful connection between the careers of two storied warships.2
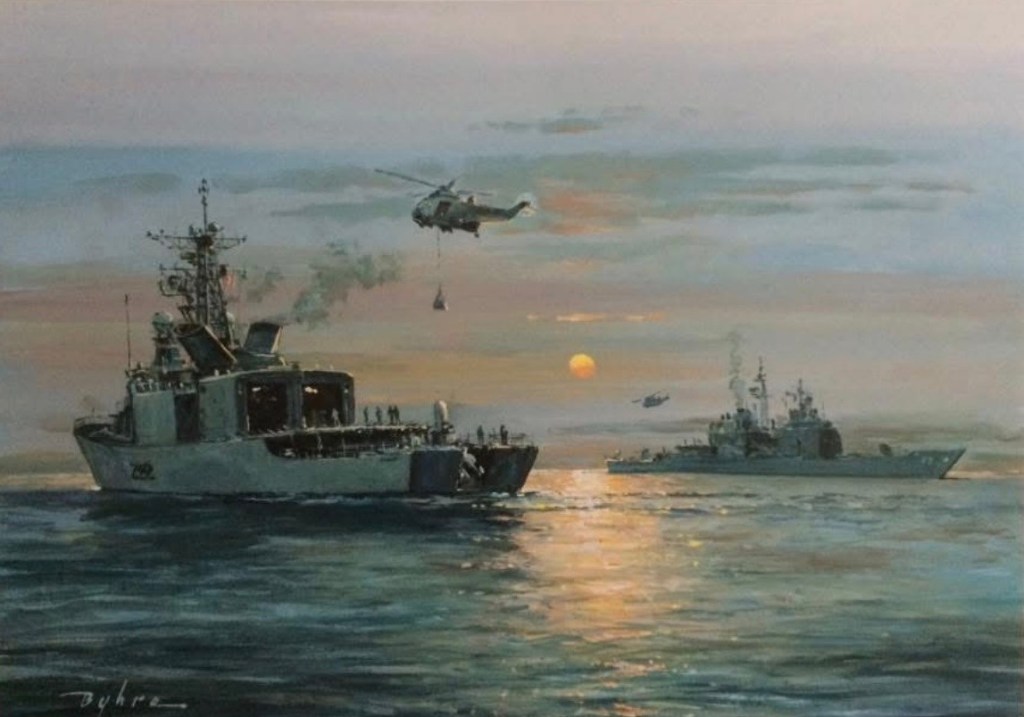

At daybreak, 18 February 1991, Captain Edward Hontz, USN, was speaking to the crew of his command, the guided-missile cruiser USS Princeton (CG-59) over the ship’s 1MC (PA system).3 The ship was crawling forwards at 3 knots through a suspected minefield, in shallow water near Falaika Island in the northern Persian Gulf. A crew member in a jury-rigged chair at the bows peered intently down into the water. Beside him, a shipmate manned a .50 caliber machine gun.

Princeton was using its AEGIS missile-defense system to protect a force of minesweepers that was tasked with clearing a corridor for Coalition ships through an Iraqi-laid minefield. There was a suspected “Silk worm” anti-ship missile site on the coast. Hontz had just notified the crew that USS Tripoli (LPH-10), an Amphibious Assault Ship, serving as flagship of the minesweeping force, had been damaged by a mine early that morning.
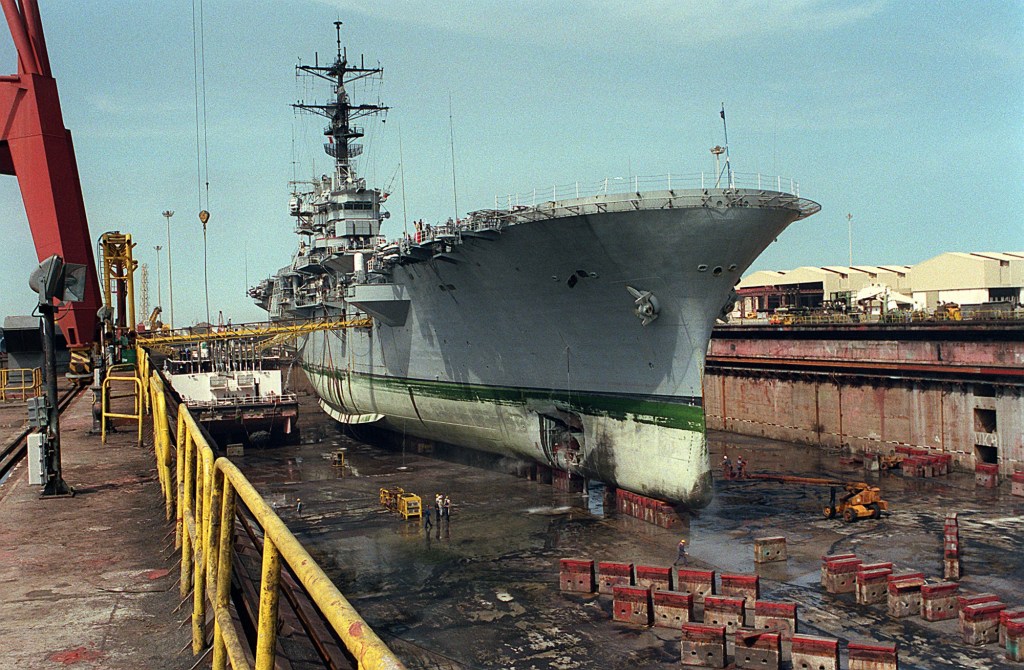

At 7:15 AM local time – just as Hontz reminded crew to remain vigilant during their current mission – a mine exploded underneath the Princeton’s port propeller and rudder. Seconds later another mine detonated off the starboard bow.4 Crew members were thrown around like rag dolls all over the ship. The up-and-down whiplash motion was especially violent at both bow and stern. This terrifying movement was joined by gut-wrenching side-to-side seesaw. The ship bent and flexed beyond what it was designed to take. Deck seams opened up, frames were fractured, the deckhouse structure cracked, and aluminum flexed and distorted. The propeller shaft was damaged and the rudder was jammed.5 As crew struggled to get to their General Quarters posts, many thought they’d be abandoning ship. The damage was serious. Miraculously, no one had been killed.6
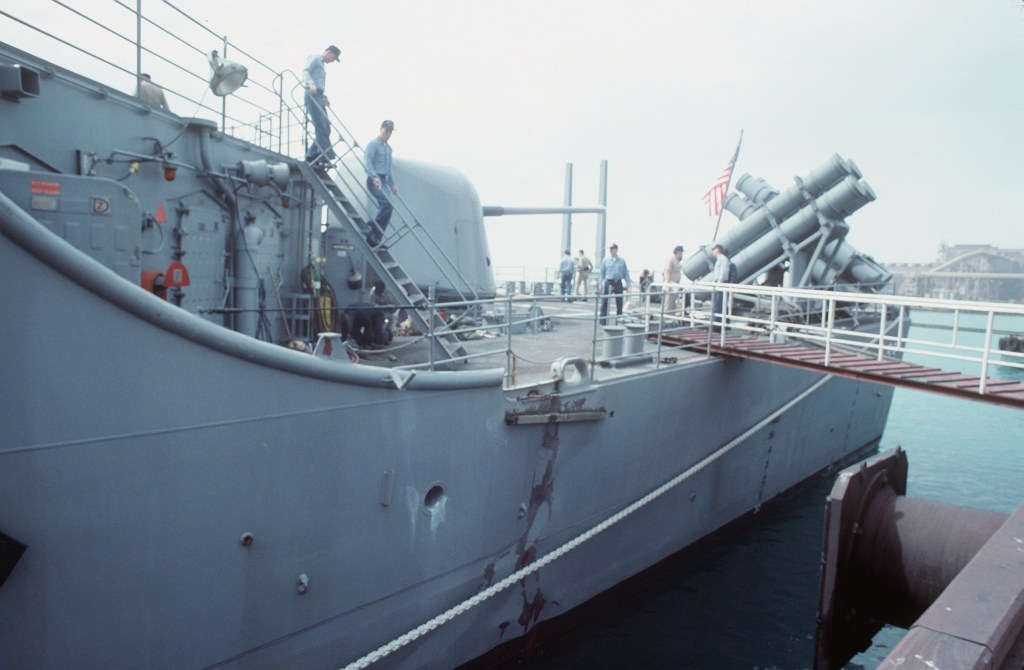

At 09:05, Commander John Pickford, RCN, aboard the Canadian Iroquois-class destroyer HMCS Athabaskan (DDG-282), received information about USS Princeton’s damage. Athabaskan was deployed to the Persian Gulf, along with HMCS Terra Nova, an older Restigouche-class destroyer, and the replenishment vessel HMCS Protecteur, as the naval component of Operation FRICTION, Canada’s military contribution to Desert Storm. Athabaskan had been operating to the south, in the central Gulf, escorting coalition vessels.
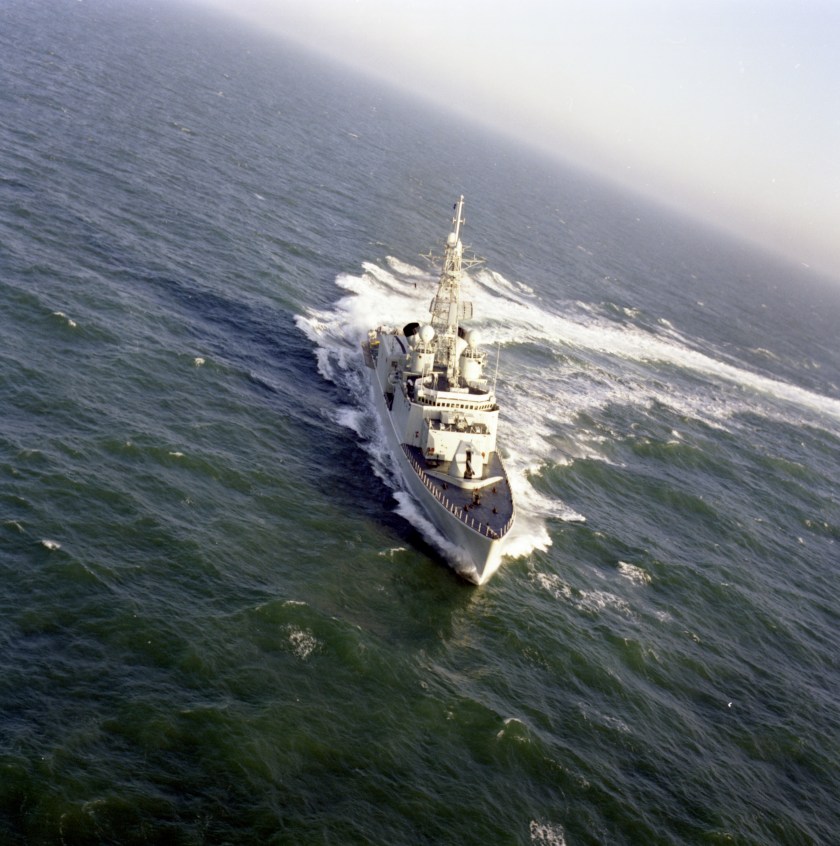

Pickford was ordered to escort the tug Smit New York to Princeton. Reportedly, Capt. Hontz had specifically requested Athabaskan’s assistance, acknowledging the usefulness of the Canadian ships’ specialized mine-avoidance sonar and the deployed air component of recently-upgraded CH-124 Sea King helicopters.7 Athabaskan had just refueled from USS Platte, “the preferred oiler of the Persian Gulf” the day before, and had received a visit from the commander of the Canadian naval forces in the region, CANCOMFORME, Commodore Kenneth Summers.
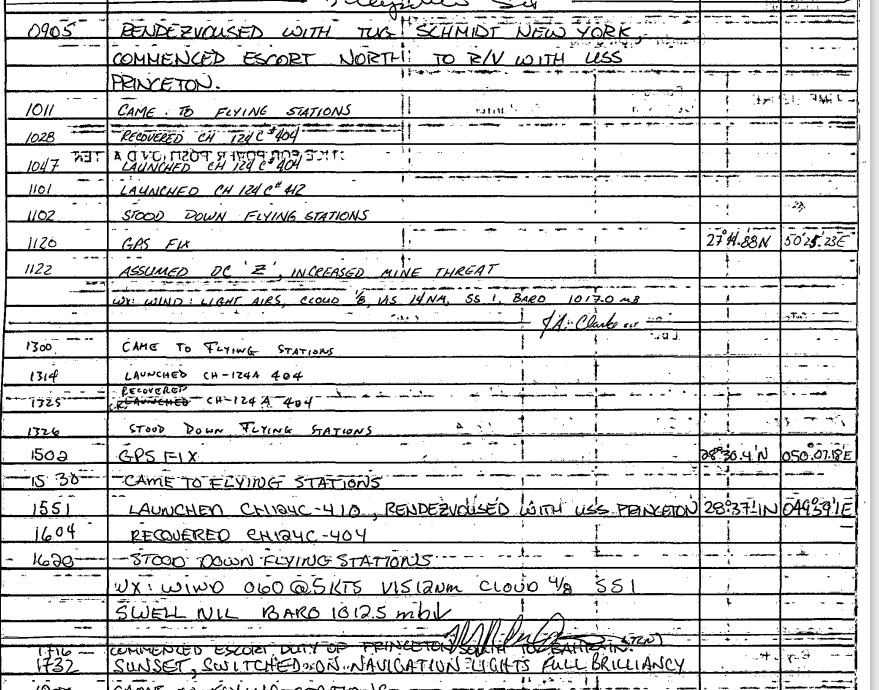
Athabaskan immediately set a course north and assumed Defence Condition “Zulu,” bringing the ship and crew to full readiness while ensuring all watertight compartments were closed. Princeton’s crew were working to contain the damage, as the few serious injuries received medevac transport. The AEGIS system had not been disabled, and the ships’ 5″ guns and the missile systems were rapidly brought back online. Athabaskan rendezvoused with Princeton at 15:51 at position 28°37′ north, 49°59′ east and commenced the escort south towards Bahrain at 17:16. The Canadians handed the escort over to the elderly wooden-hulled minesweeper USS Adroit, while the tow was take up by the salvage ship USS Beaufort. While Princeton was repaired first in Bahrain and then in Dubai, Athabaskan replenished from HMCS Protecteur and then returned to escort work in the central Gulf.8

Athabaskan’s next high-profile tasking involved escorting the hospital ships USNS Comfort and Mercy.9 As a parting gift for the exhausted crew of Princeton, a Sea King was used to “cross-deck” a pallet loaded with several cases of Labatt beer, and a bottle of Canadian Club whisky for Capt. Hontz.10

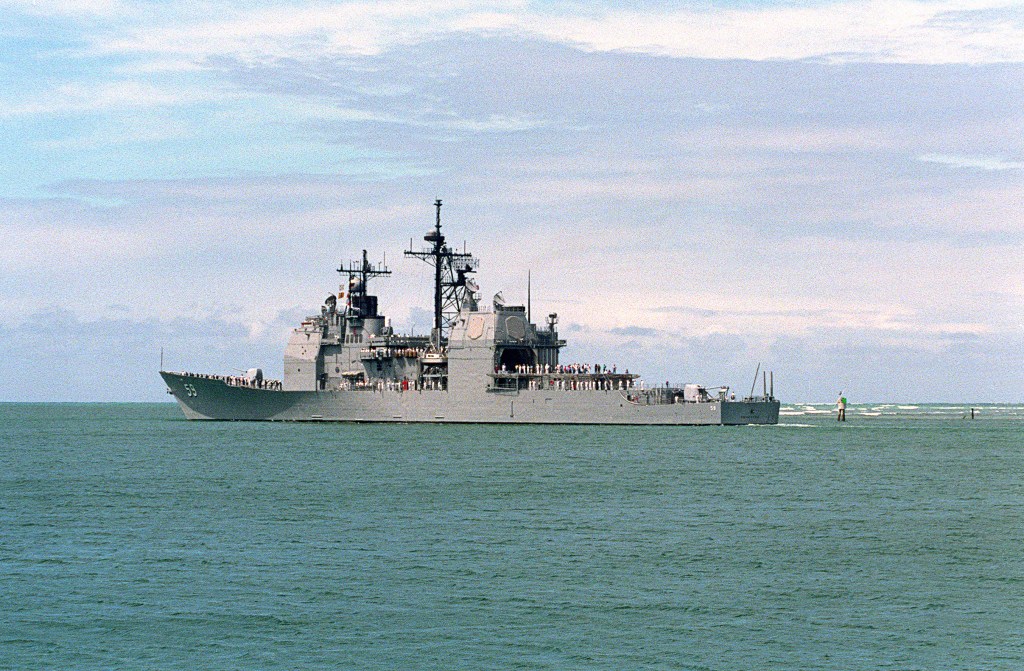
As a result of deployments to the Persian Gulf in 1990-1991, both Athabaskan and Princeton added new battle honours to the records of their illustrious forebears.11 HMCS Athabaskan served on until 2017, and was scrapped the next year.12 USS Princeton was set to rights and rejoined the US fleet, and continues to serve as one of the last Ticonderoga-class guided missile cruisers in commission.13 In Canada and the United States, former crewmembers of these outstanding vessels will continue to gather at reunions and online events, and, in their separate reminisces of their time in the Gulf, will think back to a remarkable episode of Operation Desert Storm.
